microeconomics(マイクロエコノミクス)
ミクロ経済学(みくろけいざいがく)
ミクロ経済学(英語版)
What is Microeconomics?
Microeconomics is research on whether the behavior of individuals (households and companies) brings about Optimal Resource Allocation in the market economy system.
What is households behavior?
In the market economy system, individuals act freely.
Individual freedom is to purchase goods and services so that they get income by working at their own will and maximize their utility (satisfaction) within that income.
In other words, to maximize their utility, combine "choosing to sell labor" and "choosing to buy goods and services" at their own will.
Adam Smith's "An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations"
A prominent British economist, Adam Smith (1723-1790), in 1776 announced "The Wealth of Nations".
Adam Smith's idea in "The Wealth of Nations" states that "When individuals act to maximize their utility, the power of" invisible hands "acts in the market to optimally allocate resources, The total utility (satisfaction level) of society (whole country) is maximized ". The work of "Invisible Hand" is called "Market Mechanism".
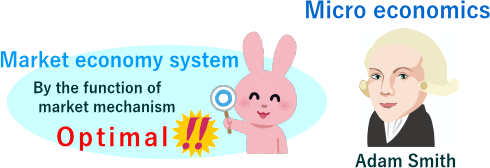
The theory of Adam Smith became the major theory of microeconomics. This is called Equilibrium Theory.
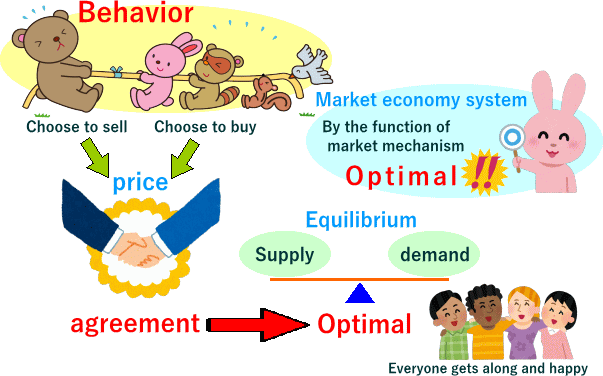
Equilibrium Theory is a theory that uses mathematics to explain that "Transactions are established where the aggregate demand and the aggregate supply are matched by the function of market mechanism, and the volume of transactions is maximized."
What is Equilibrium in microeconomics?
Equilibrium in microeconomics means the Optimal Resource Allocation (Pareto Optimum) realized when trading at equilibrium price in the market economy system.
At this time, all market participants agree to trade at equilibrium price. This means that all market participants are convinced of the way of Distribution.
Here, equilibrium can find meaning "everyone happy" in human relationships.
金融大学TOP > よくわかる!金融用語辞典 > ミクロ経済学(英語版)

 参考 :
参考 :